Customized Solutions
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)
A “Membrane Bioreactor” (MBR) processes are mainly used for wastewater treatment by using microfiltration (MF) or ultrafiltration (UF) and integrating them with a biological process like a suspended growth bioreactor. The membranes are employed as a filter removing the solids which are developed during the biological process, which gives a clear and pathogen-free product.
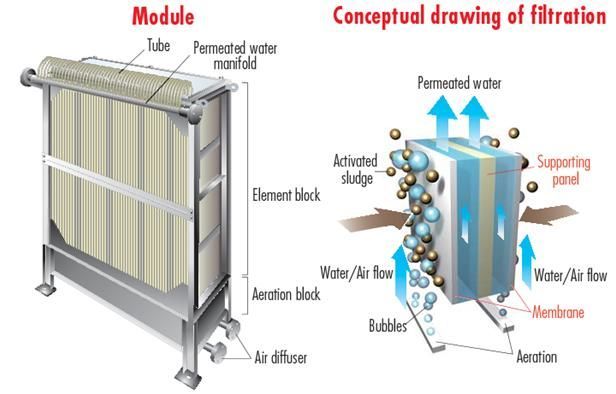
The wastewater goes through a fine screen for the removal of big objects that might cause damage to the downstream equipment. Then it enters an Anoxic Zone for the treatment of nitrogenous matter and phosphate following an Aerobic Zone where microorganisms with the help of the oxygen coming out of the FBD will digest the organics matter in the wastewater and clump together as they do so, producing a sludge. This sludge will enter the Immersed Membrane Bioreactor where the membrane will separate the solids and microorganisms from water.
A membrane bioreactor is essentially a replacement in the conventional activated sludge (CAS) system for the settlement tank for solid/liquid separation. The MBR gives the end-user improved process control and much better product water quality.
The MBR process operates over a considerably different range of parameters than the conventional activated sludge process
- SRT 5 -20 days for conventional system – 20 -30 days for MBR
- F/M 0.05 -1.5 d-1for conventional system – < 0.1 d-1for MBR
- MLSS 2,000 mg/L for conventional process – 5,000 -20,000 mg/L for MBR
In general, MBRs have three distinct membrane configurations
- Flat sheet (FS)
- Hollow fibre (HF)
- Multitube (MT)
- MBR Applications
MBRs are generally a preferred option when,
- There’s limited space
- End-user requires high quality treated water (e.g. for water reuse)
Increasingly tighter environmental regulations together with a decreasing MBR CAPEX and OPEX has led to a boost in installations and size all over the world. MBRs have now been implemented in more than 200 countries worldwide with several plants over 4,200 m3/d in capacity and their growth rates of up to 15% are regularly reported in various market analyses.
Usually, MBR technology is applied to those wastewaters with a readily biodegradable organic carbon content. The latter is especially true when it comes to the food and beverage sector which has made extensive use of MBR technologies.
Wastewaters markets which are containing sparingly biodegradable content (e.g. landfill leachate and pharmaceutical effluents) have also seen a growth of MBRs due to the long solid retention times (SRT) that allow for an improved biological treatment over the one from the conventional biological processes.
Waters that contain suspended oil (vegetable or mineral) require pretreatment (e.g. plate separation, dissolved air flotation, or both) to protect the membrane.
Although the MBR global market is mainly dominated by a few major companies, the number of technology suppliers continues to grow, with over 70 MBR membrane module products available on the market today.
In general, MBRs have been applied to treat effluent in several industrial sectors, like:
- Food and beverage − high in organic loading
- Petroleum industry − exploration, refining and petrochemical sectors
- Pharmaceutical industry – have active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)
- Pulp and paper industry − high levels of suspended solids, COD and BOD
- Textile industry effluent − re-biodegradability, toxicity, FOG content and color
- Landfill leachate − a wide variety of dissolved and suspended organic and inorganic compounds
- Ship effluents − legislative requirements and space restrictions.
- Industrial versus municipal treatment
